A frequently returning term regarding processes is called a bottleneck. This means some kind of work overload is present. When these processes are improved, more effective result can be achieved. And thereby, more profit is obtained. This is called the Theory of Constraints (ToC).
What is the Theory of Constraints?
This methodology focuses on discovering the most limitative aspect of a process. This bottleneck is then eliminated systematically. Every (complex) system consists of more than one connected activities. Sometimes it becomes hard to focus on what is really important because of this. However, the Theory of Constraints aims at focusing on the goal your organisation wants to achieve and provides you with a set of tools to do so. There are three aspects of ToC:
- The five steps of focus
Identifying and eliminating limitations. - The process of thinking
Tools for analysing and solving problems. - Throughput Accounting
Measuring performances and supporting decisions from the management team.
When analysing the processes within an organisation, there can be different types of limitations. ToC focuses on the one with the highest priority: the current limitation. Therefore, ToC tends to be the perfect methodology for the creation of fast improvements.
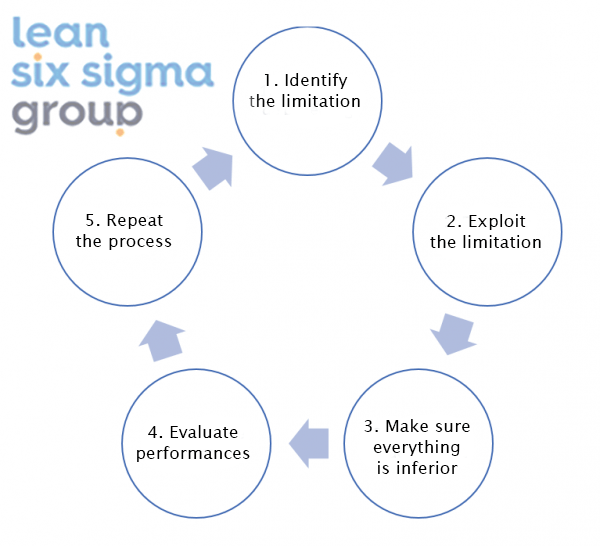
The five steps of focus
- Identify the limitation
Identify the current limitation – or bottleneck – in the process. - Exploit the limitation
Make improvements as to tuning out the limitation while using the correct resources. - Make sure everything is inferior
Take another look at all activities in the process, in order to make sure they support the needs of the limitation. - Evaluate performances
If the limitation still exists during this step, think about eliminating other activities as well. Repeat this step until the limitation is actually removed. And keep in mind this sometimes means investments should be made. - Repeat the process
These five steps of focus are walked through in a cycle In other words, when one limitation is removed, the next can be handled immediately by starting at step one again.
The process of thinking
This tool has been developed to retrieve the unwanted effect of a limitation and replace it with a new one. Three questions that should be asked to do so are:
- What should be changed?
- To what should it be changed?
- Which precise actions lead to this change?
Below, you can find some tools that can be applied to fulfill the idea of the process of thinking.
- Current reality tree
Describe the current situation. - Evaporating cloud tree
Evaluate potential improvements. - Future reality tree
Describe the future situation. - Strategy and tactics tree
Compose a plan of action regarding improvements.
Throughput Accounting
Throughput Accounting is an accounting methodology which tries to eliminate harmful disturbances. It actually arose from traditional accounting methods that threaten the profit of an organisation to decrease. ToC makes an organisation mandatory to sell the entire stock in the foreseeable future. This might lead to an increase of profit on paper, but in reality, stock takes up this profit while it is still unsold. And this same money could be used to make other investments. However, ToC finds decreasing costs less important than focusing on the flow of products.
As said, ToC focuses on throughput accounting with the most important pillars: throughput, investments and operational costs.
- Throughput
The time in which products are sold to customers. - Investments
Money that is tight to the organisation instead of usable: stock, machines, building(s), et cetera. - Operational costs
Money that is invested in the throughput of an organisation.
What are the advantages of the Theory of Constraints?
By applying ToC, the following advantages arise:
- Increase of profit;
- Quick improvements;
- Improved capacity – by eliminating constraints, an organisation becomes able to produce more and more;
- Decrease of lead time – the process flow will improve;
- Less stock – the amount of work within a process decreases.
Some examples of ‘Constraints?’
Constraints can be defined as everything that limits an organisation in its progress. In other words, it keeps an organisation from its goal(s).
- Physical
This includes actual equipment, but other tangible things such as lack of employees or space or shortage of material as well. - Policy-wise
The recommended way or working, procedures of the organisation or written agreements. - Paradigm
This category contains things such as habits. Think of “Machines should be turned on and working 24/7 in order to keep costs per product as low as possible”. - Demand of the market
When an organisation produces more than the market demand, it is categorized under demand of the market.
To conclude, the Theory of Constraints is able to assist you with solving problems regarding limitative factors within your organisation structurally. By applying this method cyclically, your organisational processes will improve continuously.





